Is Flute a Woodwind: Best Complete Guide with 3 Criteria

This guide answers “Is flute a woodwind instrument?” by exploring its history, construction and unique traits that define its place within this family of instruments. This blog post will explain why the flute is part of the woodwind family — it provides you with a complete overview of the criteria to categorize an instrument as a woodwind instrument.
What Are Woodwind Instruments?
Woodwind instruments were traditionally constructed out of wood. Today their production involves wood, metal, plastic or some combination. They have narrow cylindrical bodies featuring key holes, an opening at the bottom end and a mouthpiece at the top.

Woodwind instruments produce sound by blowing air through their mouthpiece and adjusting their pitch using finger holes. Most woodwind instruments also include metal keys to cover up their holes. Reeds (thin pieces of wood) create soundwaves to generate unique melodies.
Ranging from simple wooden whistles, woodwind instruments grew in popularity during the Renaissance and Baroque eras — recorder, oboe and bassoon dominated chamber music ensembles; later, clarinets became prominent players as music changed.
There are four broad categories for woodwind instruments: flutes (including recorders), clarinets, saxophones and double reeds. Of these instruments, flutes date back thousands of years to ancient civilizations — while clarinets date from just recently.
Is Flute a Woodwind Instrument?
The short answer is Yes!! As their names imply — woodwind instruments were traditionally constructed using wooden material.
Woodwind instruments such as flutes fall within this category since their playing technique involves controlling breath rather than lips for vibration (and sound production). Woodwinds include single and double reed instruments as well as flutes.

Musicians consider the two main categories of wind instruments — flutes and reed instruments.
A flute produces sound by blowing air into its tube and channeling surrounding air back through holes into itself — music is produced as the air passes back out through holes into itself.
Flutes and piccolos make vibrational sounds against an embouchure hole (unlike brass instruments) while clarinets use one single-reed mouthpiece. Oboes and bassoons uses double reeds.
Discovering more about the flute family? Read up on 10 Flute Members with Photos, Videos and Prices
1 The Way Flutes Produce Sound
Musical instruments are classified as woodwind or brass categories — It depends on how they “produce” sound. Brass instruments use lip vibration while woodwinds employ reeds or other means to generate tone.
In other words — Brass instruments produce sound through lip buzzing from musicians which is then amplified and channeled through its mechanism to the instrument itself.
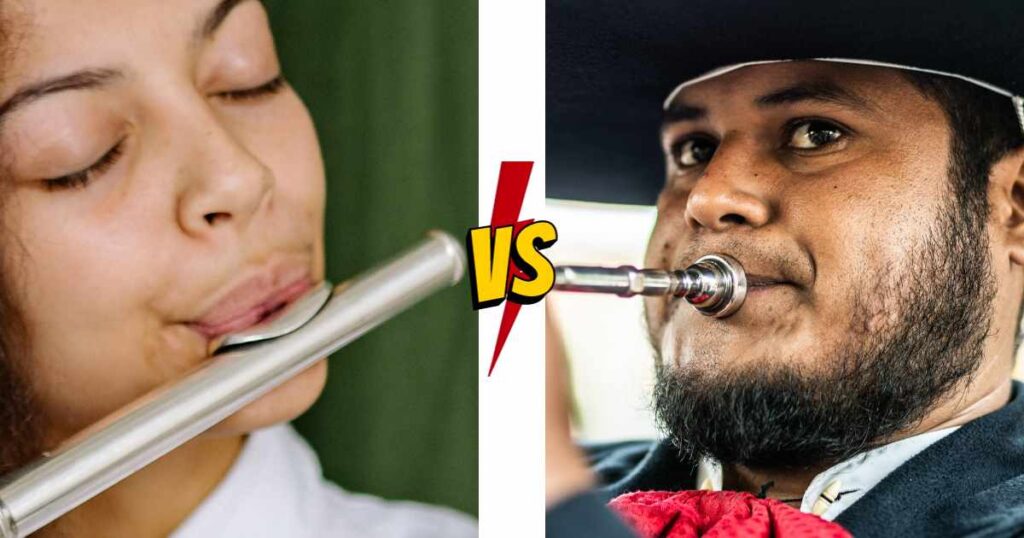

Flutes produce sound by breaking apart airstream, classifying them as woodwind instruments rather than brass. Blowing air across their lip plate causes vibrations for the sound production — musicians manipulate this instrument while its components generate its sound output.
On the contrary, instruments utilizing reeds for pitch modulation such as saxophones, clarinets, bassoons or oboes would all fall within this classification — the wind instruments.
Flute and reed instruments use similar principles of sound production despite having different mechanisms.
Single-reed instruments feature a mouthpiece equipped with a thin strip of material called a reed that vibrates upon being filled with air. When this air enters through its inlets, this sets in motion and produces sound waves from it.
Double-reed instruments (such as oboes or bassoons) operate similarly. Their mouthpieces feature two flat reeds aligned face to face and attached to a metal pipe that comes directly into their instrument.
2 How the Woodwind and Brass Instruments Change Pitch
Woodwind instruments feature keys. Users can open or close holes on the instrument’s body for airflow control and pitch alteration by pressing keys. Pressing multiple keys redirects airflow for a lower pitch.
Brass instruments use valves to alter their pitch by redirecting airflow through longer tubes, instead of creating new openings. Brass instruments adjust their tubing length for sound waves to travel before hitting their destination — typically the bell.
Not all brass instruments feature valves — the trombone (…not valve trombones) uses a slide instead. This enables players to adjust how long it takes (by increasing tubing length) for air to arrive at its bell.
Wind instruments feature multiple spaces from which sound can escape while brass instruments typically only have one. Flutes feature keys that control opening and closing holes (sometimes partially) to release air through these holes closer to their body joint — except when playing low notes which release it through the foot joint.
3 The Sound Direction
Brass instruments typically produce sound by radiating sound through their bell — as opposed, woodwind instruments produce waves of sound in all directions. Brass instruments create this difference by releasing sound from their bell — channeling all sounds in one direction.
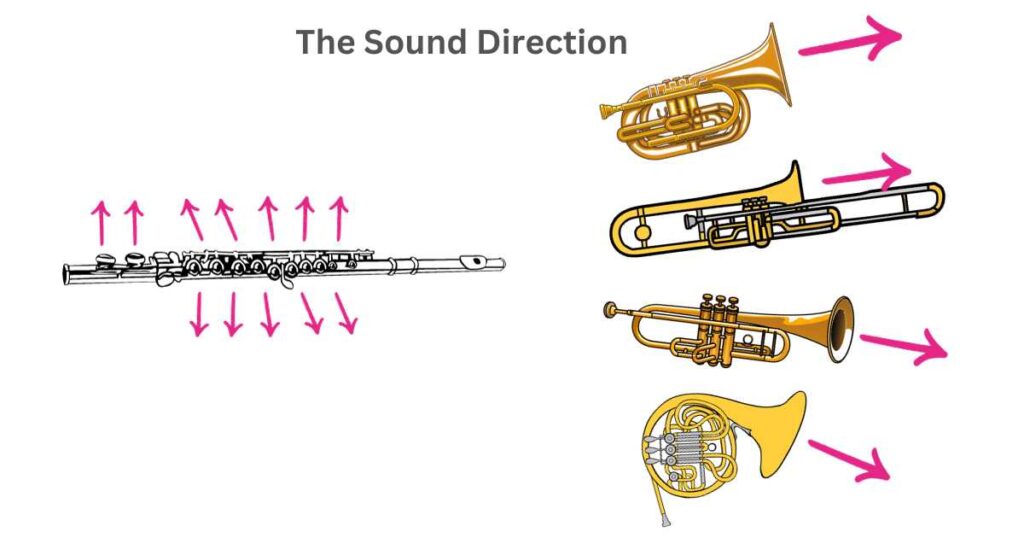
Woodwind instruments use keyholes to release sound at different points within their instrument — sound travels in all directions simultaneously. This makes woodwind instruments particularly engaging instruments to play for audiences!
As a woodwind instrument, the flute differs from brass instrument in that its sound production occurs through keys (…keyholes) instead of being projected outwards from one point.
Conical Bore Matters
Conical bore refers to the shape of an flute’s tube. It widens at the end before narrowing back down towards its center to form a cone-like appearance — called “conical.”
Woodwind instruments use conical bores to amplify sound waves while shaping mouth positioning during playback.
Other woodwind instruments
Recorder
The Recorder is an easy and enjoyable woodwind instrument with roots dating back to the 14th century. It’s perfect for beginners (or music learners) — an excellent introduction into musical genres!
It is affordable and commonly found playing early music — it also appears in contemporary recordings and film soundtracks. An ideal instrument to begin learning on for beginners or kids!!
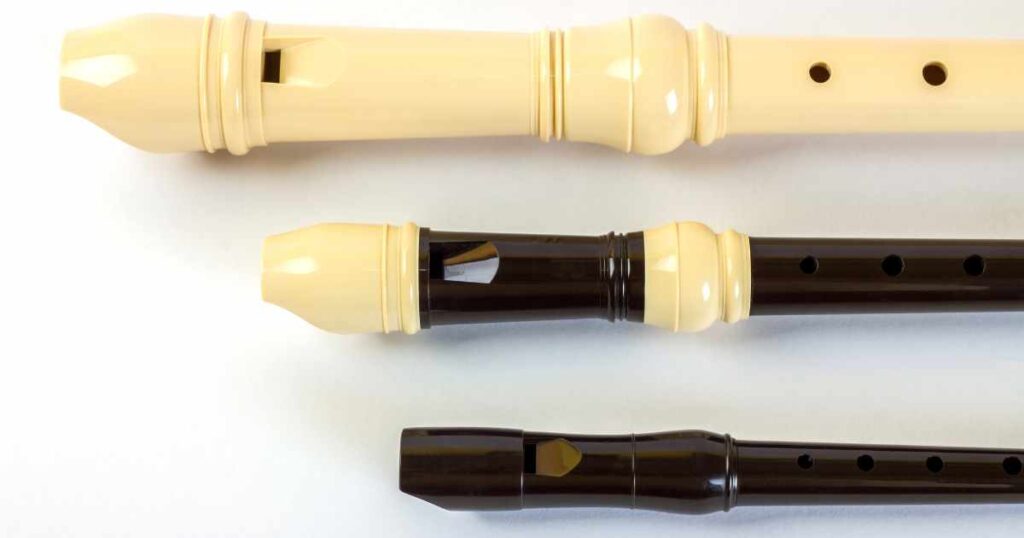

Recorders are flute-like instruments blown from one end (similar to modern concert flutes but simpler). Their tonal expressiveness is limited due to simplicity in design. Wood or synthetic resin recorders come in various sizes — Bass, Tenor, Alto, Soprano and Sopranino. They come with Baroque or German style fingering techniques — each offers advantages when performing music.
Clarinet
A clarinet features a cylindrical wood body fitted with one single-reed mouthpiece. With warm, sweet tones, it’s ideal for jazz, classical, and pop music applications. The clarinet’s range has four octaves (the highest among wind instruments!!) and is pitched at B flat key (Soprano).
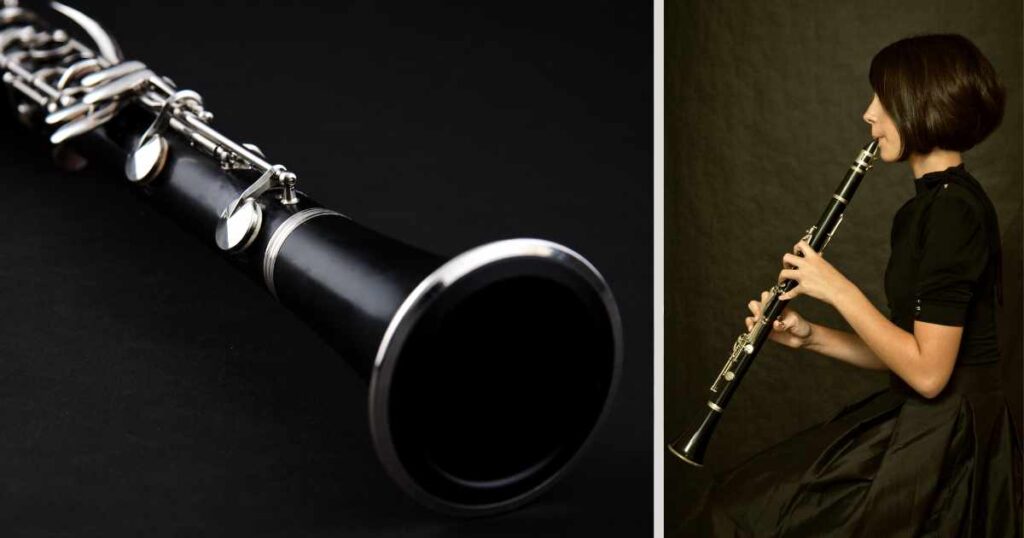

The standard B flat clarinet is by far the most widely-played clarinet variant. There are also other clarinet variants such as the Alto clarinet and Bass clarinet with lower pitches; the bass clarinet is one octave below Soprano.
These woodwind family instruments resemble their saxophone counterparts when played properly.
Saxophone
The saxophone is an impressive woodwind instrument renowned for its distinct, brassy sound produced. To play it, the player blows air through one single reed while manipulating fingerings to produce various notes — its two-and-a-half octave range will leave audiences breathless!
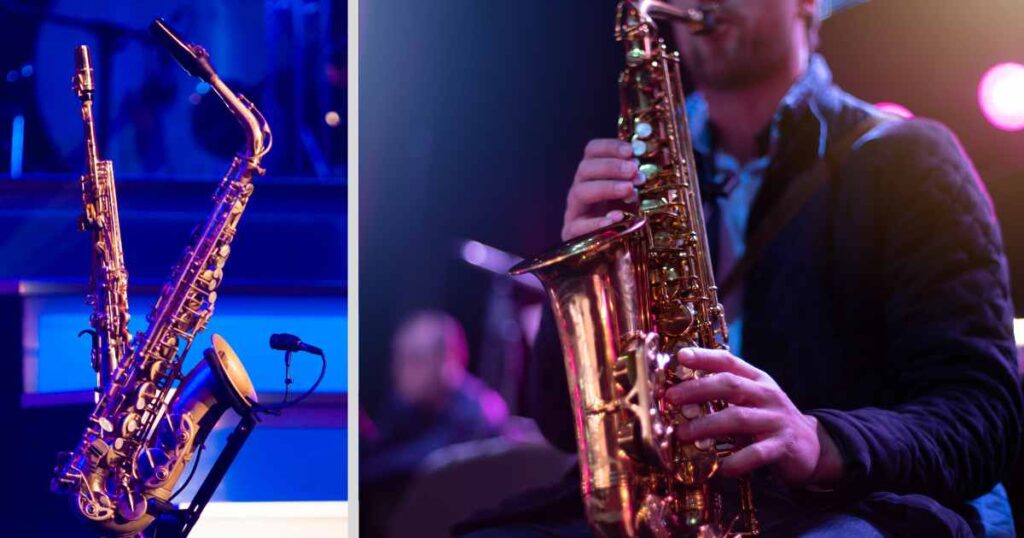

Saxophones come in several sizes, such as — Soprano, Alto, Tenor and Baritone Saxophones.
Saxophone’s versatility extends far beyond woodwind ensembles — it is frequently featured in brass instrument ensembles, marching bands, jazz and blues music performances.
Oboe
The oboe is a cylindrically, double-reed instrument with a melodious and expressive sound. The instrument’s double reed features two thin strips that vibrate against each other to produce its beautiful tone.
The oboe is a challenging yet rewarding instrument. Commonly found in orchestras and smaller ensembles seeking romantic or dreamlike soundscapes.
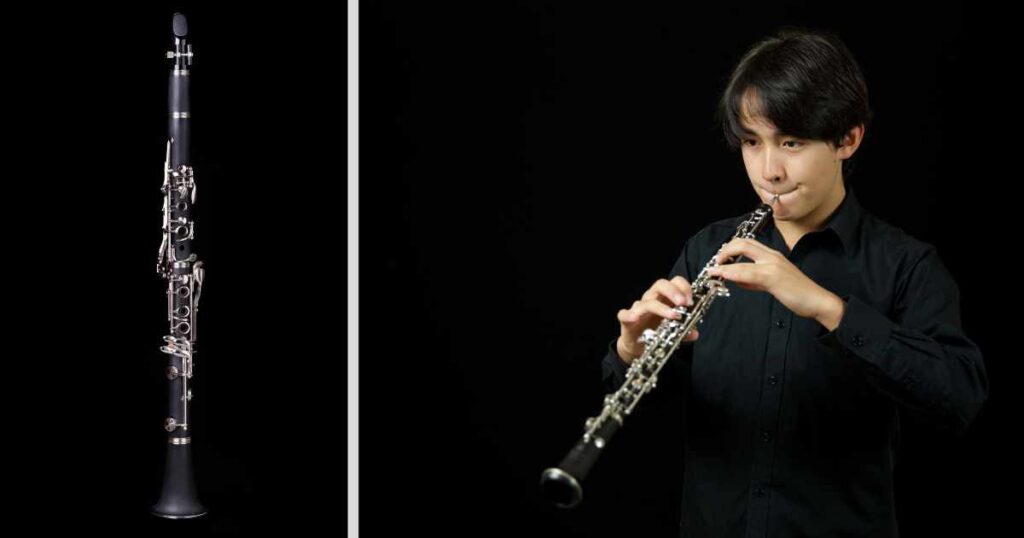

Manipulate holes and keys within an oboe’s range for different notes produced within its repertoire.
The oboe is a transposing instrument — the oboe plays sounds other than what it’s written notation. The main key is C with two and a half octaves range between — F4 to B flat5.
Bassoon
The bassoon belongs to the woodwind family and can be among the MOST challenging instruments to learn!! A bassoon has a double-reed mouthpiece and a long, conical bore for creating its distinct deep sound.
The bassoon’s keys and mechanisms come with 22 individual keys — letting players play different notes…
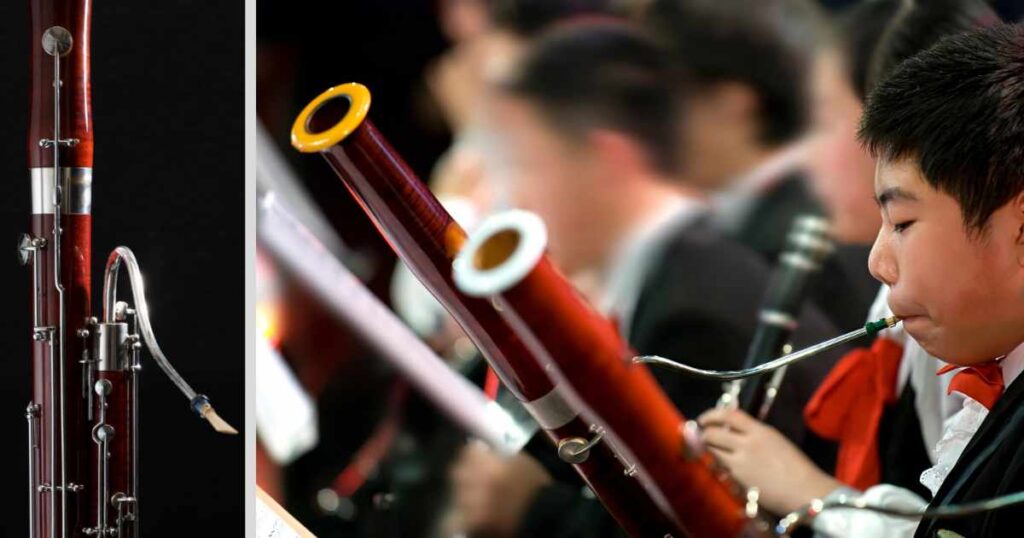

The bassoon is widely renowned for its dark rich sound. A bassoon uses the bocal — its unique mouthpiece to achieve its signature tone.
A bocal is a curved metal tube that attaches the reeds to the bassoon body and sits atop it. Bassoon bocals have distinct styles that affect tone quality, articulation and response!!
Bocals come in different lengths and thicknesses for bassoonists to select — each has an influence over playing style and tone quality.
Conclusion: Is flute a woodwind?
The flute is an impressive instrument with centuries of history behind it. Belonging to the woodwind family due to its construction and sound production capabilities, its unique tone and melodic capabilities distinguish itself as part of this category of instruments like clarinets or saxophones.
Do you want to learn to play the flute — Check out this post with 8 Helpful Tips of How to Play the Flute